Will AI replace humans in the future of design?
- Nov 07 2024
- 1 views

There has been a wide fear for years that robots will dominate the world someday. They are said to take away jobs, especially ones requiring manual labor. However, many designers believed their careers were immune to automation because they also required intellectual force besides manual one. So, is it proven or not? Let’s figure out how artificial intelligence which crunches numbers like a piece of cake is going to be able to design.
There was a surprising development wherein Artificial Intelligence (AI) made its way into the field of design. Mattel, for instance, uses AI technology in product design while interior designers are creating mockups with AI that can detect can change floors, walls, and furniture. Nestle utilized an AI-enhanced Vermeer painting in marketing one of their yogurt brands, and BBDO experimented with Stable Diffusion in producing materials.
However, for fields like web design with clearly defined mediums, the question arises: how does AI come into play? This article will focus on the history of AI in web design, its current impact on creativity, and tips for web designers to remain pioneering.
1. The glorious history of AI in web design
The abilities of AI that were described earlier have their roots in development that dates back fifty years. These capabilities have been rapidly advancing in recent years thanks to more advanced computation models, increased amounts of training data to refine these models, and enhanced computing power to run them.
In 1950, the founder of modern computer science, Alan Turing, posed a famous question: Can machines think? this question prompted research into teaching machines human knowledge using declarative rules, but this approach ultimately proved challenging due to the numerous implicit rules that govern our daily lives.
During the 90s, feeding knowledge was replaced by a data-focused approach. Specifically, scientists started developing computer programs that could learn from vast amounts of data using neural network structures, similar to the functioning of the human brain. This innovation led to notable achievements such as IBM’s Deep Blue breaking the world record at chess in 1997, and Google Brain’s deep neural network with the capability to identify and classify objects.
In recent years, there have been advancements in neural network model sophistication, data source, and computing power that helped to boost machines’ abilities. For instance, the first generative adversarial neural network was produced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, allowing machines to produce new data that had similar statistics as the original dataset. This discovery paves the way for AI models like DALL·E 2, StableDiffusion, and MidJourney in 2022, which demonstrate original creations abilities outlined at the beginning of the article.
2. The current situation of AI’s contribution
Nowadays, there are usually six phases that both designers and clients go through collaboratively to create a new website. The word "client" has a broad meaning and may include teams within a company working on their own website or an individual in charge of developing a website independently.
- Forming: The designer works with the client to decide on the concept for a website design.
- Defining: The designer collects all the necessary requirements and creates a project plan to fulfill them.
- Ideating: The designer came up with ideas adjusted based on the requirements.
- Socializing: The client consults the opinion of designers and gives feedback or chooses from the given ideas.
- Implementing: The designer produces high-quality designs that are subsequently transformed into code for deployment.
To gain a deeper comprehension of how AI affects design fields, how AI deals with distinct tasks involved in the five steps will be scrutinized below.
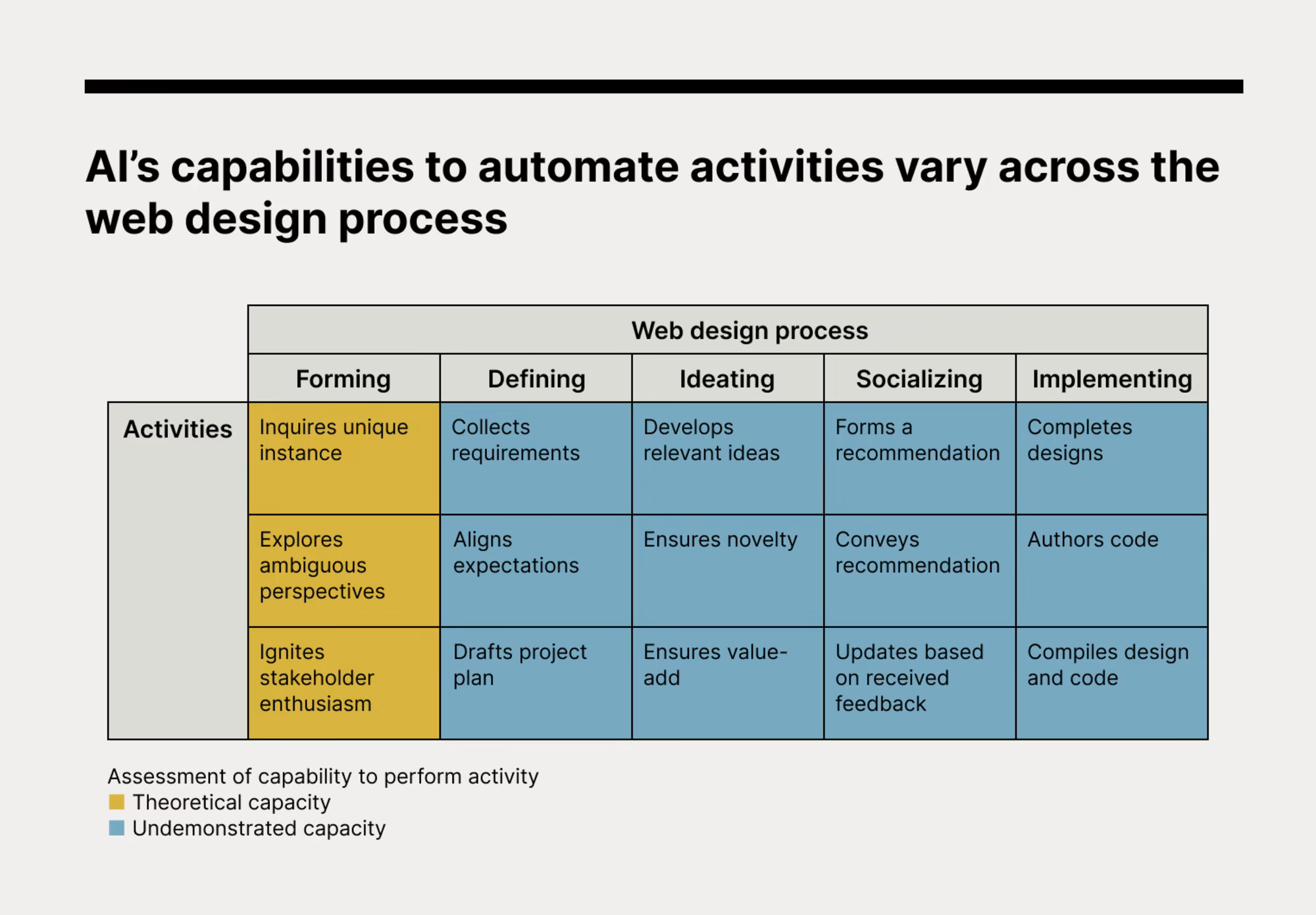
FORMING #
To form, the designer needs to investigate the particular scenario, explore debatable viewpoints, and motivate stakeholder involvement.
Investigates the particular scenario: Unproven capability.
When accepting a new project, it's crucial to comprehend the client's distinctive context and determine if web design is the appropriate choice to help businesses reach their goal. However, current AI models struggle with analyzing subjects that are not included in their training data sets. Since it's impractical to gather comprehensive data on every business, it's evident that current AI models are not capable of investigating each unique scenario thoroughly.
Explore debatable viewpoints: Unproven capability.
At the start of a project, it's vital to consider various perspectives and use them to guide exploration. For instance, a designer may learn about a brand's emotional stories and utilize that knowledge to inform the appropriate website redesign. While AI models from institutions like MIT and Microsoft have demonstrated early potential in recognizing abstract concepts and comprehending emotions, they still lack the ability to fully embrace human perspectives. According to a recent Harvard Business Review article, empathy is still a crucial missing element in today's AI models.
Motivates stakeholder involvement: Unproven capability.
To ensure a project's success, both the designer and client must be enthusiastic and dedicated to seeing it through to completion. While AI has demonstrated potential in creating copy that appeals to customers and persuades them to make a purchase, it remains unproven when it comes to sparking enthusiasm for long-term business engagements that require sustained effort and input.
DEFINING #
At this stage, designers are required to gather specific orders, set expectations, and draft a project plan.
Gather specific orders.
To gather comprehensive requirements, clients should articulate their technical specifications, page count, and launch dates. AI models are now capable of performing this task, with Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) enabling them to parse, understand, and respond to inputs based on examples of human exchanges. OpenAI's ChatGPT, for example, can ask for additional context, answer follow-up questions, and reject inappropriate requests. AI models are already being used for customer service and have demonstrated positive results in terms of trust and satisfaction.
Aligns expectations: Theoretical capacity
To ensure that the client and designer have the same expectations, they should agree on acceptance standards and communication schedules. AI models are now able to facilitate this alignment by autonomously handling negotiations. Research from Meta (formerly Facebook) demonstrates that AI models can use simulation and prediction to complete negotiations independently. In the business world, companies like Pactum are using their proprietary AI models to assist global retailers in obtaining the best possible terms in B2B purchases.
Drafts project plan: Theoretical capacity
For a project to be kept on track, the designers are supposed to set milestones and deadlines. AI models can currently estimate the length of tasks and the sequencing of activities in a project. In 2017, a machine learning algorithm named Support Vector Machine was exhibited with the function of precisely forecasting project timelines.
Additional research has demonstrated the use of Artificial Neural Networks for defining task connections and generating charts of work breakdown structures (WBS).
IDEATING #
To generate ideas, the designer must create concepts that meet predetermined standards, ensure they are novel to help identify the client and ensure they are useful to promote the client's business objectives.
Develops relevant ideas: Theoretical capacity
The designer should ensure that their generated ideas are in line with the previously agreed criteria. Advanced AI models such as OpenAI's DALL-E 2 can create output that aligns with prompt criteria through machine learning. This enables the AI to generate design ideas, including UI design, that meet the prompt criteria.
Ensures novelty: Theoretical capacity
To ensure that generated ideas are original, AI models use diffusion techniques to create novel outputs. These techniques involve scrambling and reassembling learned data to generate new data that bears some resemblance to the learned data. This allows AI models to create new ideas by combining aspects of what they have learned, much like humans combine known concepts to create new ideas. Google's Imagen Video, Meta's Make-a-Video, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion are all examples of AI models that use these techniques to generate completely new output.
Ensures value-add: Theoretical capacity
The generated ideas should provide additional value to the client, and AI models are well-suited for this task as they can surpass or match humans in this regard. This is due to their ability to learn from vast amounts of data and their unmatched computing power to identify patterns, making AI a powerful tool for generating, enhancing, and energizing ideas that can offer added value, which might be difficult for humans to achieve on their own.

SOCIALIZING #
Socializing calls for the designer to form a recommendation, convey the recommendation, and respond to feedback.
Forms a recommendation: Theoretical capacity
It's important for designers to have their own perspectives on the ideas they're working on. Nowadays, AI models can assess different options by assigning scores to them. By utilizing datasets that monitor design and user engagement, AI models can learn to assess and prioritize design options based on how likely they are to enhance conversions. Nevertheless, it remains to be seen if AI models can effectively evaluate more subjective and emotionally-driven goals.
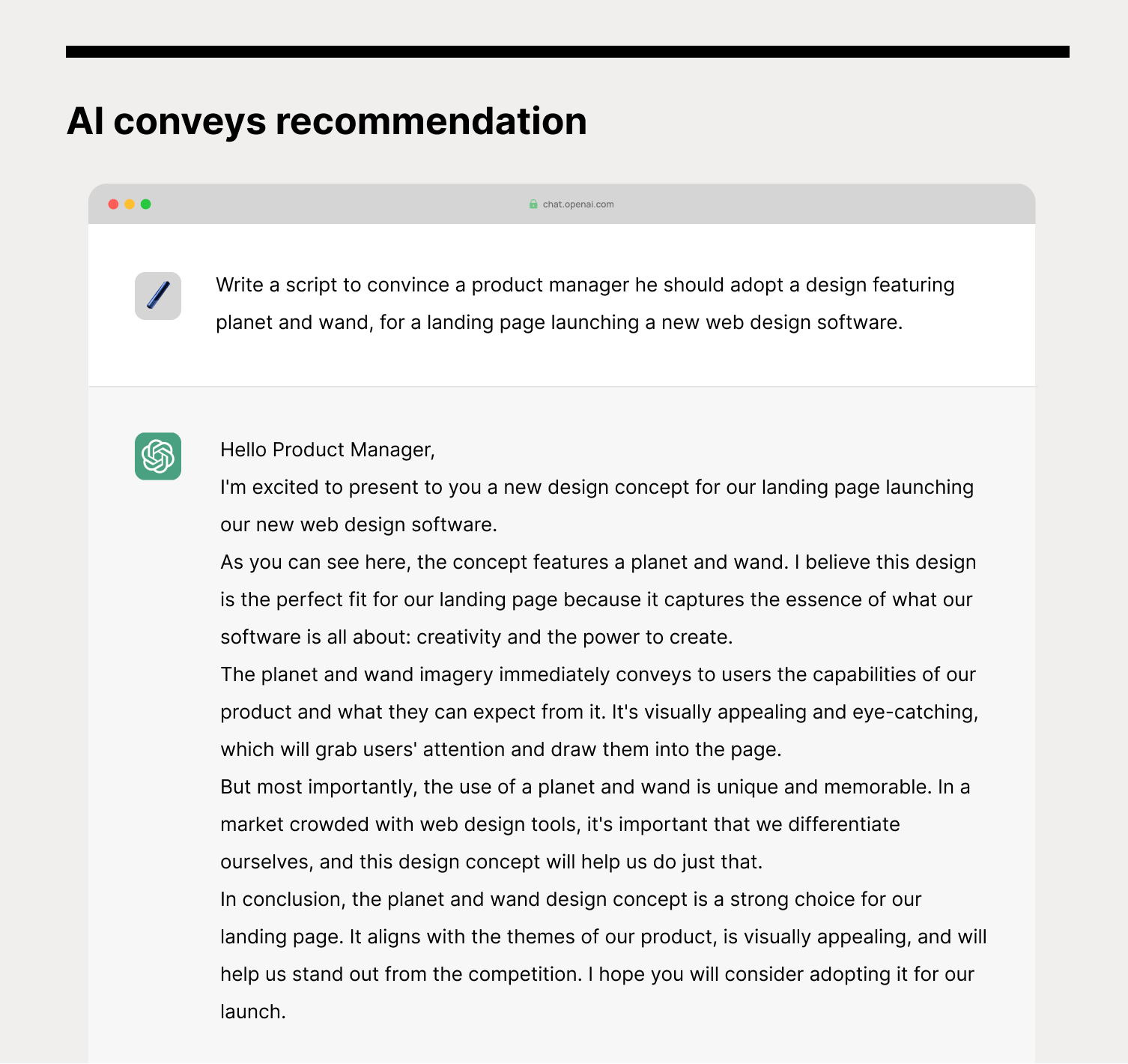
Conveys recommendation: Theoretical capacity
The designer must create a convincing story to help the client make a decision. AI models have demonstrated the ability to generate compelling narratives that can assist with decision-making, similar to humans. For instance, IBM Research's Project Debater can produce relevant arguments that support particular positions. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of AI models in finding the right balance between assertiveness and dominance in real-world scenarios is still being researched.
Updates based on received feedback: Theoretical capacity
A designer should listen to client feedback to make necessary adjustments. AI models, such as DALL-E 2 and ChatGPT, can also use feedback to enhance their performance. These models can improve their outputs by updating the input prompts with feedback. However, when feedback includes unfamiliar concepts, textual inversion techniques can be employed to help the model learn and integrate these new concepts into its output.
IMPLEMENTING #
It is expected of the designer to create designs, write code, and integrate both into a website that is functional.
Completes designs: Theoretical capacity
Once a decision has been made, it is important to develop creative directions that align with that decision. Nowadays, AI models are capable of completing designs based on either textual or pictorial input. These models utilize machine learning techniques to identify relationships between input prompts and outputs and then use that information to generate a completed design output that matches the input. There are already models being researched that can return medium-fidelity mockups by detecting and refining UI elements on low-fidelity sketches. In deployment, OpenAI's Outpainting feature is able to extend original designs and produce stunning results, such as extensions of Johannes Vermeer's Girl with a Pearl Earring scene. It is not too far-fetched to imagine that, given the demonstrated capabilities of current models, web page designs could be automatically generated based on the style of a specific section from a design proposal.
Authors code: Theoretical capacity
AI models have the potential to generate HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code based on functionality descriptions. These models have been trained on vast amounts of data that demonstrate the relationship between descriptions of functionality and the corresponding code that implements it. By learning from this data, AI models can produce code that accurately implements the desired functionality. For instance, Microsoft’s PowerApps software features an assistive function that turns natural language into ready-to-use code for querying. According to the VP of GitHub Next, which researches emerging technologies in software development, coders will soon be able to sketch the architectural design, describe the functionality, and let AI fill in the details. While the human review is still required for output from models today, continuous feedback loops are expected to result in a continual improvement in quality.
Compiles design and code: Theoretical capacity
The process of compiling the chosen idea requires the alignment of both design and code. AI models, with their capabilities in design and coding, can potentially automate this process. OpenAI engineers have already demonstrated technologies that allow for the creation of simple apps by describing what is required, such as a personal website with PayPal embedded for payments. This signals a potential future where individuals with ideas can easily bring them to life, known as the "Gutenbergian" future.
3. The Future of AI’s Role in the Design
The use of technology in the field of design is well-known, and designers have always been pioneers in utilizing their potential to innovate and expand their abilities. Just like how the printing press in the late 15th century encouraged scribe artists, textile machines in the 19th century encouraged artisans, and photo-editing software encouraged darkroom artists to shift their focus, we can expect a similar shift brought on by AI in the 21st century.
With AI's potential to take on various tasks in the web design process, it is likely that later stages of design will become more automated. Therefore, designers who want to remain productive and relevant will need to focus their creativity on earlier stages of the process, where they can differentiate themselves from replaceable tasks.
We don’t expect this creative shift to happen overnight but gradually in three waves. Although AI models have shown potential in web design tasks, more industry-specific data will be needed to ensure their reliable use. Increasing the quantity of training data will improve their accuracy in tackling abstract and general problems in the field. Looking at the broader picture, we will explore how automation in web design may evolve over time and its effects, with the goal of providing guidance to practitioners in managing this upcoming future.
WAVE 1: DESIGN COPILOT #
The wave refers to how AI models can help designers with tasks that used to be manual and time-consuming. These tasks will mainly be low-level and specific. Because of this, AI models will need less training data, and the output will consistently meet expectations due to the controlled domain. We are currently at the beginning of this shift, with technology previews from Adobe and other startups. Possible future examples include tools that automatically adapt designs for different screen sizes, add suggested animations for interactivity, and complete complex formatting adjustments with descriptive prompts.
WAVE 2: GENERATION AND MANAGEMENT #
The second wave of AI in web design will involve the generation of semi-completed designs and client relationship management. This includes ideating and implementing output ideas, which require higher levels of abstraction in a narrow scope. While current models like ChatGPT and DALL·E 2 can generate design suggestions and outputs as images, more training with web design-specific datasets is needed to improve variation and quality. However, there are also ethical concerns regarding issues such as copyright.
In addition, management tasks such as defining and socializing ideas involve lower abstraction but a wider scope. Successful use cases in other industries exist, but their implementation in everyday account management will require additional oversight to strike a balance between persuasion and tactful communication.
WAVE 3: AUTOMATION #
The third wave pertains to full automation of the entire web design process, which includes assisting in the development of strategy and intent during the Forming stage. Although there have been efforts to incorporate AI modules into website builders, there are still challenges that need to be addressed, such as the integration of uniquely human perspectives like empathy. It will take additional time and effort to overcome these challenges before AI can completely replace the contribution of a designer.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into the design world has created an array of possibilities. Generative models, for instance, have demonstrated theoretical capabilities and practical applications across various stages of web design.
Despite the absence of some uniquely human capabilities, such as empathy and inquisitiveness, AI designers can leverage technology to achieve unprecedented levels of creativity. The collaboration between designers and AI is comparable to a brush stroke on a blank canvas, creating something truly extraordinary. The future of design is set to be brighter as designers and AI work together to push the boundaries of creativity. So, let's give AI a chance to be the right-handed partner for designers, helping them to create better results and save less effort.

